Learn the differences between these two anticoagulants with Picmonic.
Some topics you will learn in this infographic:
Suppresses Coagulation:
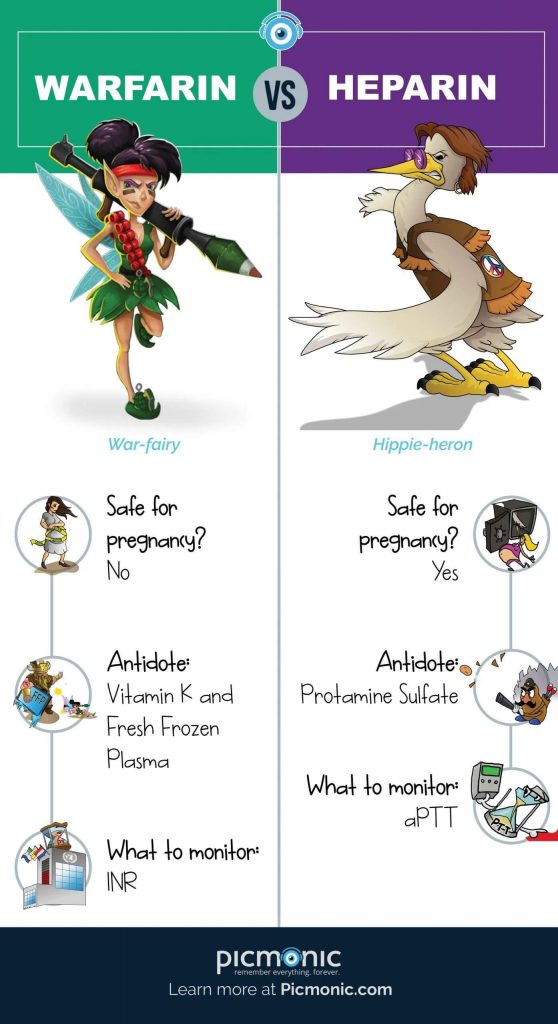
Heparin activates antithrombin, which inactivates thrombin and factor Xa to suppress the formation of fibrin. Fibrin is the main component of thrombi found in the veins; therefore, heparin can be very effective in the management and prevention of venous thrombosis.
Preferred (Safe) During Pregnancy:
Pregnant women requiring anticoagulant therapy should be given heparin (unfractionated) over Coumadin. This is because heparin does not cross the placenta or cause harm to the developing fetus. This should be used cautiously, as maternal osteoporosis and thrombocytopenia are possible side effects.
Chronic Anticoagulation:
This medication is used to decrease the tendency to form or to prevent clots in patients at risk for their formation. Common ailments requiring chronic anticoagulation include atrial fibrillation, artificial heart valves, previous pulmonary embolism and previous deep vein thrombosis.
Necrosis:
Though rare, warfarin necrosis is a very serious side effect seen in patients taking this medication and leads to massive thrombus formation, causing skin necrosis and gangrene. This side effect stems from the initial inhibition of proteins C and S, leading to a prothrombotic state when starting this medication. Patients who are protein C deficient are more susceptible to this effect.
To learn more, get started with a free Picmonic account.